SpyCloud Report: 61% of Data Breaches in 2023 Were Malware Related
Average identity has 1 in 5 chance of already being victim of infostealer malware infection
AUSTIN, Texas–(BUSINESS WIRE)–SpyCloud, the leader in Cybercrime Analytics, today released its 2024 SpyCloud Identity Exposure Report, an annual report examining the latest trends in cybercrime and their impact on individuals and organizations. SpyCloud researchers recaptured 43.7 billion distinct identity assets in 2023, including nearly four times more personally identifiable information (PII) assets than in 2022 — over 32 billion, compared to last year’s 8.6 billion.
Taking a deeper look into how stolen data empowers bad actors to perpetrate cybercrimes including account takeover, fraud, and ransomware, SpyCloud researchers analyzed the exposures of the average digital identity being traded in the criminal underground and found that the average identity appears in as many as nine breaches and is associated with 15 breach records.
The rise in identity-based attacks can be attributed to a rapid increase in malware. SpyCloud found that 61% of data breaches in 2023, involving over 343 million stolen credentials, were infostealer malware-related. Of these compromised identity records, one in four contained information about the user’s network or physical location, putting the individual’s identity, platforms they have access to, and physical well-being at risk.
Researchers also found that the average identity had a 1 in 5 chance of already being the victim of an infostealer infection. Infostealer malware enables criminals to collect vast amounts of information about the user and the device, including a user’s session cookies, API keys and webhooks, crypto wallet addresses, and more. This stolen authentication data enables cybercriminals to bypass protections including MFA and even passkeys to hijack their victim’s identity and take over digital sessions.
“Cheap and easy-to-use infostealers combined with the ubiquity of stolen data online can make cyber defense seem like an impossible task,” said Trevor Hilligoss, VP of SpyCloud Labs, SpyCloud’s research team responsible for recapturing data and analyzing patterns from the criminal underground. “Protecting digital identities and beating cybercriminals at their own game requires a multi-layered approach. It starts with quickly identifying exposed identities and immediately moves to post-infection remediation – invalidating compromised authentication data for all applications exposed by the infection. It’s a sure-fire way to prevent future cyberattacks resulting from the stolen information.”
SpyCloud researchers also recaptured nearly 200 different types of PII in 2023, ranging from full names (3.16 billion) and phone numbers (2.14 billion) to dates of birth (920.25 million), social security and national ID numbers (171.61 million) and credit card numbers (36.97 million).
Additionally, mobile malware is becoming an attractive attack vector for criminals. Between August and December 2023, SpyCloud recaptured 10.58 million mobile records exfiltrated by malware. While the goal of mobile malware is often financial fraud, compromised devices can also result in sensitive data compromise, disruption of operations, and reputational damage.
“Cloud applications, mobile devices and online services have become essential to both our personal and professional lives. When you consider the vast amounts of information that we put online and the likelihood of that information ending up in the wrong hands, our digital valuables have evolved beyond traditional credentials,” said Damon Fleury, Chief Product Officer of SpyCloud. “Threat actors are linking together identity records from hundreds of sources to impersonate their victims, making it extremely difficult for platforms to differentiate between legitimate users and criminals.”
Additional key findings from the 2024 report include:
Poor password hygiene persists with pop culture still influencing password choices.
- SpyCloud recaptured nearly 1.38 billion passwords circulating the darknet in 2023, an 81.5% year-over-year increase from 759 million in 2022.
- Within these passwords, the report finds a 74% password reuse rate for users exposed in two or more breaches in the last year—a 2 point increase from the prior year.
- Pop culture continues to drive popular password choices.
- 1.1 million passwords were related to American fantasy football.
- 1.1 million were related to the Hollywood writers’ strike.
- 1 million were related to the NBA playoffs.
- Passwords influenced by artists such as Shakira (508,000), Miley Cyrus (257,000), and Taylor Swift (119,000) were also common.
The U.S. government continues to struggle with bad password practices.
- SpyCloud researchers found 723 breaches containing .gov emails in 2023, up from 695 in 2022 and 611 in 2021. The recaptured records contained over 281,000 .gov credentials.
- The most common passwords associated with .gov emails were password, pass1, and 123456.
- Password reuse rates for .gov users increased this year, rising to 67% from 61% in 2022.
The most noteworthy data leaks recaptured by SpyCloud last year:
- WhatsApp: 364 million records leaked
- Twitter (now X): 203 million records leaked
- Luxottica: 203 million records leaked
- UnionPay China: 127 million records leaked
To view the full report, visit spycloud.com.
To learn more about SpyCloud Labs’ analysis of active cybercriminal tactics, visit https://spycloud.com/resources/spycloud-labs/.
About SpyCloud
SpyCloud transforms recaptured darknet data to protect businesses from cyberattacks. Its products operationalize Cybercrime Analytics (C2A) to produce actionable insights that allow enterprises to proactively prevent ransomware and account takeover, safeguard employee and consumer identities, and investigate cybercrime incidents. Its unique data from breaches, malware-infected devices, and other underground sources also powers many popular dark web monitoring and identity theft protection offerings. SpyCloud customers include half of the ten largest global enterprises, mid-size companies, and government agencies around the world. Headquartered in Austin, TX, SpyCloud is home to more than 200 cybersecurity experts whose mission is to make the internet safer with automated solutions that help organizations combat cybercrime.
To learn more and see insights on your company’s exposed data, visit spycloud.com.
From WindowsReport.com: The states at the highest risk of cyber attacks
The states at the highest risk of cyber attacks
- Nevada is the state where you are at the highest risk of a cyber-attack, with 300 victims per 100,000 people
- Delaware and Alaska take second and third, respectively
- Alabama residents lost the most money on average to cybercrime in 2022
New research has revealed the states at the highest risk of cyber-attacks, with Nevada coming out on top.
The research by tech experts at WindowsReport.com analyzed data from the FBI’s 2022 Internet Crime Report to see which state had the highest amount of cybercrime victims per 100,000 people and which states saw victims lose the most money on average.
The study found that residents in Nevada are at the highest risk of cyber attacks. The 2022 report found 9,090 cybercrime victims last year in the state, which is around 300 victims per 100,000 people when accounted for population numbers. Total victim losses in 2022 amounted to a massive $127,315,394, a loss of $14,006 per victim on average.
Coming in second place is the state of Delaware, with cybercrime in the mid-Atlantic state affecting 241 of every 100,000 people, with 2,327 victims recorded last year. Total losses added up to $40,980,800, an average loss of $17,611 per victim.
Taking third place on the list is the northwest state of Alaska. The state saw 1,539 victims of cybercrime in 2022, which is around 209 victims per 100,000 people. Victim losses amounted to $16,826,999, with each victim losing an average of $10,934.
Colorado comes in fourth place on the list, with 209 cybercrime victims per every 100,000 people and 11,683 victims recorded in 2022. Victim losses added up to $178,389,862 last year, each losing $15,269 to cybercrime on average.
Rounding out the top five is the state of California, which saw the highest recorded number of cybercrime victims in 2022, with 80,766, and comes in fifth place is 204 victims per 100,000 people.
| # | State | Population | Number of cybercrime victims in 2022 | Cybercrime victims per 100,000 people | Total victim losses in 2022 | Average amount lost per victim |
| 1 | Nevada | 3,034,392 | 9,090 | 300 | $127,315,394 | $14,006 |
| 2 | Delaware | 967,171 | 2,327 | 241 | $40,980,800 | $17,611 |
| 3 | Alaska | 737,438 | 1,539 | 209 | $16,826,999 | $10,934 |
| 4 | Colorado | 5,695,564 | 11,683 | 205 | $178,389,862 | $15,269 |
| 5 | California | 39,557,045 | 80,766 | 204 | $2,012,806,866 | $24,921 |
| 6 | Florida | 21,670,000 | 42,792 | 197 | $844,972,494 | $19,746 |
| 7 | Maryland | 6,042,718 | 11,644 | 193 | $217,880,447 | $18,712 |
| 8 | South Dakota | 882,235 | 1,691 | 192 | $48,072,730 | $28,429 |
| 9 | Indiana | 6,691,878 | 11,682 | 175 | $73,678,120 | $6,307 |
| 10 | Arizona | 7,171,646 | 12,112 | 169 | $241,191,959 | $19,913 |
Alabama is the state where individual victims lost the most to cybercrime on average. With a total of $247,930,058 lost to 4,893 victims, each cybercrime victim lost roughly $50,670 on average in 2022. However, with just 100 victims per every 100,000 people, the state comes in 43rd on the list of all states.
With cybercrime becoming as common as it is, it’s important to understand the ways you can protect yourself, and doing things such as keeping up to date on data breaches, using strong passwords, not trusting unsolicited emails or messages and using an effective anti-virus software can all keep you well protected in the current climate.”
Commenting on the findings, a spokesperson for WindowsReport.com said: “If your state doesn’t appear on the list, it doesn’t necessarily mean you’re not at risk either, and it’s still important to be cautious online with how clever scams are getting nowadays. This is especially true when dealing with transactions of large sums of money, which is evident with some of the huge victim losses across all states.”
ENDS
KuppingerCole Analysts predicts Container Security Market to grow to 2.63 bn USD by 2025
In light of the growing demand for securing digital services, the Container Security Market is steadily growing and is expected to reach 2.63 billion USD by 2025. Its Compound Annual Growth Range (CAGR) of 25.7% is a key indicator of that growth. The largest market share is in North America, contributing 68.1% of the global revenue, followed by EMEA with a 25.4% share. APAC and LATAM show lower adoption, but see significant growth can be expected in those markets as well.
Read the full article here.

In the last few years, security faced a massive change in infrastructure and a major increase in overall complexity, introducing numerous new risks and security challenges. Similarly, companies must gain skills to efficiently mitigate those risks. Containers and Kubernetes have quickly become synonymous with modern DevOps methodologies, continuous delivery, and deployment automation and are generally praised as a breakthrough in developing and managing cloud-native applications and services.
However, the need to secure containerized applications at every layer of the underlying infrastructure (from bare-metal hardware to the network to the control plane of the orchestration platform itself) and at every stage of the development lifecycle (from coding and testing to deployment and operations) means that container security must cover the whole spectrum of cybersecurity and then some.
KuppingerCole Analysts is an international and independent IT-analyst organization headquartered in Europe with presence worldwide. The company provides market sizing information and reports for IAM, Cybersecurity and Digital Identity Market, assuring a neutral position with extensive expertise and practical relevance.
SMS phishing (smishing) attacks more than doubled year-on-year in 2021
In The Human Factor Report 2022, security vendor Proofpoint found that SMS phishing (#smishing) attacks more than doubled year-on-year in 2021. The report is based on their analysis of over 2.6 billion email messages, 49 billion URLs, 1.9 billion attachments, 28 million cloud accounts and 1.7 billion mobile messages.
The study details most common attack surfaces and methods including categories of risk, vulnerabilities, attacks, Russian Aligned APT’s, and Privilege as a vector.
Key Findings:
- 50% – Managers and executives make up only 10% of users, but almost 50% of the most severe attack risk
- 100k – Attackers attempt to initiate more than 100,000 telephone-oriented attacks every day.
- Malicious URLS are 3-4x more common than malicious attachments.
- Smishing attempts more than doubled in the U.S. over the year, while in the U.K. over 50% of lures are themed around delivery notification.
- More than 20 million messages attempted to deliver malware linked to eventual ransomware attack
- Data loss prevention alerts have stabilized as businesses adopt permanent hybrid work models.
- 80% of businesses are attacked by a compromised supplier account in any given month.
- 35% of cloud tenants that received a suspicious login also saw suspicious post-access activity.
Experts with Dispersive Holdings and Veridium offer perspective:
Rajiv Pimplaskar, CEO, Dispersive Holdings, Inc.:
Human factor:
- “Supply chain attacks via software or hardware vendors as well as 3rd party vendors are a skyrocketing risk during 2022 and beyond. Therefore, it’s no surprise that 80% of businesses are attacked by a compromised supplier account on a monthly basis. Businesses should urgently look to bolster 3rd or nth party connections as well as remote access with strong identity verification to mitigate this threat.”
Nation State:
- “2022 year to date has been underscored by increased nation state involvement and the cyber cold war intensifying. The nation state involvement within these proxy conflicts as a means of destabilizing global and particularly western activities is a serious threat as such threat actors are highly motivated and sophisticated and are able to breach most conventional cyber defenses with relative ease. Businesses particularly within the critical infrastructure sectors should consider bolstering their cyber capabilities with more advanced military grade solutions such as a next gen VPN that offers heightened protection.”
Damon Ebanks, VP Marketing, Veridium:
“Cybercriminals continue to rely on human interaction to click malicious links, download dangerous files, inadvertently install malware, transfer funds, and disclose sensitive information. The security of an organization can be addressed by tackling the password issue head-on by completely removing passwords from the equation.
“By eliminating the use of knowledge-based authentication users cannot share credentials and phishing attacks cannot capture passwords (since there are none to expose). Brute force attacks are ruled out because bad actors can’t guess a password that doesn’t exist, and keyboard recorders can’t capture password information. Password-less authentication is of interest to all types of organizations, public and private, regardless of where they are on their digital transformation journey.
“The global pandemic has amplified the need for simple and secure access for employees, customers, and partners because these groups now work or operate from any location that can’t be secured by IT security. With the surge in gas prices remote work will remain the norm and a world where zero trust is the only solution will remain. We are living in a world where Passwordless authentication should be the norm.”
Emotet has spiked upwards
Deep Instinct released its new #Emotet findings in a blog, breaking down its latest spam and credential stealing campaigns from March 2022, even noting how TrickBot has offered assistance.
- Emotet has spiked upwards 27,00% in Q1 of 2022 compared to Q4 of 2021 and primary targets have been located in locations such as Japan, Italy, and the U.S.
- There’s been nearly a 900% increased in the use of Microsoft Excel macros compared to Q4 of 2021
- 9% of threats are unknown, never-before-seen threats while 14% of the email malware has bypassed at least one email gateway security scanner before it was captured
- 45% of the malware detected were utilizing some type of office attachment and the most common attachments used to deliver malware were spreadsheets (33%), executables and scripts (29%), archives (22%), and documents (11%)
- Almost 20% of all malicious samples were exploiting a 2017 Microsoft vulnerability (CVE-2017-11882)
Top Threats to Cloud Computing Pandemic Eleven
Release Date: 06/06/2022
Working Group: Top Threats
https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/artifacts/top-threats-to-cloud-computing-pandemic-eleven/
Armorblox Publishes Email Security Threat Report
Armorblox just launched its inaugural Email Security Threat Report. Analyzing the #email traffic of more than 58,000 organizations from Q1 2021 through Q1 2022, the research reveals:
- 87% of #Credential Phishing attacks looked like legitimate common business workflows.
- 74% of #BEC attacks used language as the main attack vector.
- 70% of Impersonation emails evaded email security controls.
- 53+% year-over-year rise in BEC attacks.
Countdown to Ransomware: Analysis of Ransomware Attack Timelines
Key Highlights
The average duration of an enterprise #ransomware attack reduced 94.34% between 2019 and 2021:
- 2019: 2+ months — The TrickBot (initial access) to Ryuk (deployment) attack path resulted in a 90% increase in ransomware attacks investigated by X-Force Incident Response (IR) in 2019.
- 2020: 9.5 days — Increased initial access broker economy and RaaS industry built upon a repeatable ransomware attack lifecycle established in 2019. Efficiencies adopted such as the ZeroLogon vulnerability to obtain privileged access to Active Directory and CobaltStrike as the C2 framework.
- 2021: 3.85 days — Large scale malspam campaigns such as with BazarLoader and IcedID and increased speed to transition access to ransomware affiliates like Conti.
Overview
IBM X-Force analyzed the evidence from multiple ransomware attack investigations that occurred between 2019 and 2021. In each investigation, access to the victim network was obtained through an initial access broker (initial access brokers are cybercriminals who specialize in breaching companies and then selling the access to ransomware attackers). The emphasis of the research was to better understand the duration of the activities during the various stages of a ransomware attack.
The findings of this research revealed the average duration of an enterprise ransomware attack (time between initial access and ransomware deployment) reduced 94.34% between 2019 and 2021. This is a substantial reduction and while ransomware attack lifecycle time decreased significantly, the research did not reveal substantial changes in the tools, techniques and procedures used by threat actors.
Additionally, X-Force analyzed victim organizations’ ability to prevent, detect, and respond to ransomware attacks prior to the deployment of the ransomware and found that ransomware attacks have continually been successful against organizations who have not implemented effective measures to combat the threat of ransomware.
Instead, the evidence revealed the time in transferring access from the access broker to an interactive session to carry out the ransomware attack has decreased significantly, and ransomware operators have become more efficient in gaining privileged access to Active Directory and deploying the ransomware. Understanding the speed and efficiency of ransomware attacks enables organizations to develop a detection and response strategy that is specifically designed to address the ransomware threat.
Initial Access Broker Ransomware Relationship
Initial Access Brokers (IABs) are criminal groups that obtain access or credentials to organizations and then sell that access to other cybercriminals for profit. IABs can obtain various levels of access in a victim network, ranging from credentials to remote services such as virtual private network (VPN), remote desktop protocol (RDP), web shells, and use malware such as TrickBot, Dridex, Emotet, or Buer Loader to establish foothold in a victim network.
In 2019, a relationship between Emotet, TrickBot, and Ryuk ransomware was discovered, where the Ryuk ransomware operators were granted access to an organization through a TrickBot infection. The TrickBot to Ryuk attack path resulted in a 90% increase in ransomware attacks investigated by X-Force Incident Response (IR) in 2019. As the Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) model increased in popularity through 2020, the relationship between other first-stage malware and ransomware attacks were established such as, Dridex malware to BitPaymer ransomware or Gootkit malware to REvil ransomware.
Throughout 2021, the ransomware affiliate Conti exploded in popularity and have been associated with obtaining access through Emotet and IcedID infections.
How Ransomware Attacks Happen
In November 2021, X-Force released research detailing how most ransomware attacks occur in a predictable five-stage pattern: Initial Access, Post-Exploitation Foothold, Reconnaissance/Credential Harvesting/Lateral Movement, Data Collection and Exfiltration, and Ransomware Deployment.
Understanding the Adversary: How Ransomware Attacks Happen
While no two ransomware incidents are identical, by analyzing the evidence across all ransomware-related investigations where initial access was obtained via an IAB, X-Force identified four core objectives that enabled the ransomware operators to advance through the 5 stages of a ransomware attack.
- Establish interactive access
- Move laterally
- Obtain privileged access to Active Directory
- Deploy ransomware at scale
While data theft does occur in most ransomware attacks, evidence of data theft and the duration of data theft activities are limited in many investigations. X-Force was unable to draw any concrete conclusions on the time ransomware operators spent on this stage of the attack.
Download the Definitive Guide to Ransomware
Ransomware Attack Timelines
To learn more about the timeframes involved with a successful ransomware attack year over year, X-Force researchers mapped evidence recovered during X-Force incident response engagements to points in time when the Initial Access Broker first obtained a foothold within the target network as well as when the adversary completed each of the four core objectives of the ransomware attack.
” alt=”” aria-hidden=”true” />
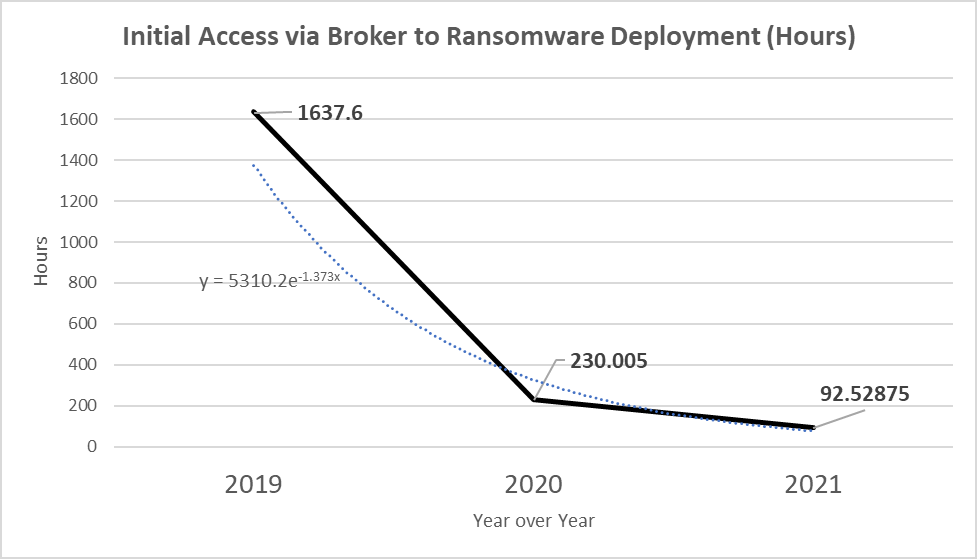
Figure 1: Trendline detailing the reduction in time from initial access to ransomware between 2019 and 2021
In 2019, the average ransomware attack took 1,600 hours or over two months from initial access to ransomware deployment. From this data, X-Force observed the longest attack timeline to be nearly eight months or 5,000 hours. The evidence revealed the longer attack timelines were primarily due to the criminal group TrickBot gaining access to and persisting in environments for the significant duration before passing access to a ransomware operator. Once that access was transferred, ransomware operators were able to deploy Ryuk ransomware and complete the attack on an average of 26.22 days (624 hours).
In 2020, there was a dramatic increase in RaaS activity resulting in ransomware engagements making up 23% (an increase of 20% from 2019) of all incidents responded to by X-Force. From these engagements, Sodinikibi/REvil prevailed to be the most common ransomware variant involved. X-Force analysis of the 2020 incidents revealed, evidence of initial access was obtained through various initial access malware including IcedID, Gootkit, Valak, TrickBot, QBot, and Dridex indicating more RaaS affiliates opting to purchase initial access rather than obtaining independently.
In addition to an increase in the number of ransomware attacks, the speed and efficiency of ransomware attacks increased significantly between 2019 and 2020. In 2020, the average ransomware attack took 9.5 days — a stark 85.96% reduction from 2019. X-Force uncovered significant reductions in the time it took to achieve each of the four core objectives enabling the ransomware operators to advance through the stages of a ransomware attack quicker. One factor that increased both speed and efficiency of ransomware attacks in 2020 was the rapid adoption of the ZeroLogon vulnerability (CVE-2020-1472) to obtain privileged access to Active Directory and CobaltStrike as the C2 framework.
Increased speed and efficiency trends in ransomware attacks continued throughout 2021, and the average time to execute an enterprise ransomware attack was reduced to just 3.85 days and X-Force observed significant reductions in both how quickly access was transferred from the broker to the ransomware operator, and how rapidly the ransomware operator was able to obtain privileged access to Active Directory. Analysis of the ransomware incident evidence indicates that the reduction in time from broker to ransomware operator is likely due to large-scale BazarLoader and IcedID infection campaigns and broker relationships with the Conti ransomware.
” alt=”” aria-hidden=”true” />
Figure 2: Trendlines detailing the reduction in time to complete each of the four core objectives between 2019 and 2021
Tools Techniques and Procedures
While analyzing the attack timelines and durations to complete objectives, X-Force conducted further analysis on the tools, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of the ransomware operators to determine if any significant advancements occurred to reduce the time to complete the attack lifecycle.
In 2019, the majority of ransomware investigations were associated with an initial TrickBot infection resulting in a Ryuk ransomware attack. In these attacks, Empire was the most frequent tool leveraged for interactive access (37% of all interactive session tools observed).
Through analysis of 2019 lateral movement and ransomware deployment techniques leveraged by ransomware operators, X-Force discovered a heavy reliance on RDP, server message block (SMB) and remote procedure calls (RPCs) communications between workstations and servers in an Active Directory environment where access to Domain Admin (DA) credentials granted the operator privileged access to all systems within the domain.
Ransomware operators relied heavily on Mimikatz to obtain privileged access to the Active Directory. Mimikatz accounted for 72% of credential harvesting activities.
” alt=”” aria-hidden=”true” />
Figure 3: 2019 top tools and techniques to achieve core objectives in ransomware attacks
In 2020, the number of tools leveraged for interactive access increased and CobaltStrike replaced Empire as the most popular interactive session tool. However, reliance on RDP, SMB/RPC, and default DA domain-wide permissions remained vital for the ransomware operators to move laterally and deploy the ransomware.
Ransomware operators were aided in obtaining privileged access to Active Directory with the release of the ZeroLogon exploit, which was rapidly adopted by ransomware operators in Q4 of 2020. However, Mimikatz still played a significant role across ransomware attacks in 2020 accounting for 53% of all credential harvesting activities.
” alt=”” aria-hidden=”true” />
Figure 4: 2020 top tools and techniques to achieve core objectives in ransomware attacks
2021 ransomware attacks continued where 2020 left off, with ZeroLogon highly utilized to obtain privileged access during the first quarter of the year, however as organizations patched the vulnerability, the operators shifted back to acquiring credentials through the operating system.
One behavioral change that was observed by X-Force was a decrease in Mimikatz usage and an increase in operators acquiring credentials from the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) process within Microsoft Windows. Based on the evidence, X-Force believes the ransomware operators began utilizing LSASS to acquire credentials as a stealthier alternative to Mimikatz. CobaltStrike usage continued to increase from 2020 to 2021 accounting for 50% of interactive session activity in ransomware attacks.
While there was some minor modifications to the tools and techniques throughout 2021, X-Force observed that ransomware attacks continued to rely upon many of the same protocols and default permissions utilized in 2019 and 2020 to achieve their goal.
” alt=”” aria-hidden=”true” />
Figure 5: 2021 top tools and techniques to achieve core objectives in ransomware attacks
Ransomware Readiness
To assess the ransomware readiness of the victims and determine if the increasing speed of ransomware attacks is due to increased sophistication to bypass security controls or detection and response solutions, X-Force compared the existing security controls and detection and response capabilities of the victims against the fundamental components of the X-Force’s ransomware readiness model.
X-Force differentiates protective and detection/response by the following conditions:
A protective control are design implementations aimed that preventing an attack from occurring or proceeding to the following stages of the attack lifecycle.
A detection and response control are technical solutions designed to detect and take action upon attacker activities as the attacker attempts to proceeding through the stages of the attack lifecycle.
Ransomware Protective Controls
X-Force identified five fundamental security controls specifically targeted to disrupt the ransomware attack lifecycle:
- Restrict and Implement MFA and PAM for Privileged Accounts
- Prohibit Workstation Logon with Domain Admin Credentials
- Restrict SMB/RDP/RPC for Internal Communication
- Implement Managed Service Accounts
- Restrict Software Execution on Domain Controllers and Secure Administrative Systems
See Controls section at the end of this report for detailed explanations for each of the aforementioned security controls
Results
X-Force discovered that in all of the successful ransomware attacks between 2019 and 2021, only one victim organization had implemented any of the five fundamental security controls specifically targeted to disrupt the ransomware attack lifecycle indicating that victim organizations have not adopted sufficient protective measures.
Ransomware Detection and Response Capabilities
To determine if the lack of adoption of detection and response capabilities played a significant role in the acceleration of the ransomware attack lifecycle, X-Force assessed the victim’s ability to detect and respond to ransomware operators in their environment before the ransomware was deployed.
To assess the ability of the victim to detect ransomware operators based on the known ransomware operator TTPs, X-Force measured the number of successful ransomware attacks vs the ability of the victim to monitor endpoint visibility either through an endpoint, detection, and response (EDR) solution or centralized logging of detailed information about process creations, network connections, and changes to file creation time.
To assess the ability of the victim to respond to ransomware operators based on the known ransomware TTPs, X-Force measured the number of successful ransomware attacks vs how often responders were able to recover alerts of the attack prior to the ransomware deployment within the client’s existing security tooling.
Results
X-Force determined that while detection capabilities increased throughout 2019 and 2021, it appears to have had little impact in slowing down the ransomware attack lifecycle. It is important to note, that while analyzing successful ransomware attacks vs detection capabilities, X-Force continually uncovered evidence of misconfigurations and oversights (Example: detect only policy vs blocking) within the tooling that enabled the attacks to progress without interruption. Additionally, X-Force discovered that responders were able to recover more alerts within existing security tools (including EDR) over the years between 2019 and 2021 indicating that security tooling has increased in volume and ability to detect ransomware operators prior to deploy of the ransomware but victims did not build out effective response policies and procedures to act on these detections.
” alt=”” aria-hidden=”true” />
Figure 6: Detection and response capabilities for successful ransomware attacks 2019-2021
Conclusions
The results of this analysis indicate that the ransomware attack lifecycle has not experienced a great deal of innovation over the years. Furthermore, the reductions in attack timelines are likely due to the operationalization of ransomware attacks within the ransomware affiliates and execution against organizations that have yet to implement protection, detection, and response solutions designed to combat the ransomware threat.
Considering the trends observed through the analysis of ransomware attack timelines, X-Force maintains that ransomware attacks will continue to increase in speed and efficiency throughout 2022. X-Force recommends organizations properly invest in protection, detection, and response efforts to effectively combat the increasing speed of the attack lifecycle.
IBM X-Force
If you have questions and want a deeper discussion about ransomware prevention, detection, and response techniques or learn how IBM X-Force can help you with incident response, threat intelligence, or offensive security services schedule a follow-up meeting here:
For more information about IBM ransomware protection solutions visit the IBM Ransomware Solutions Landing Page.
If you are experiencing cybersecurity issues or an incident, contact X-Force to help.
US hotline 1-888-241-9812 | Global hotline (+001) 312-212-8034
Learn more about how to protect your organization with the new Definitive Guide to Ransomware.
Controls
Restrict and Implement MFA and PAM for Privileged Accounts
A critical first step within this control is to establish a least privilege model within the organizations to prevent privilege escalation and credentials harvesting which is often to a critical step in a domain-wide compromise. X-Force recommends all organizations remove local administrator rights for all accounts unless absolutely necessary.
If privileged access is required for any system or systems within the organization, X-Force recommends organizations implement the following controls to address the threats of privileged account compromise.
The threat landscape has significantly evolved in recent years and X-Force no longer considers passwords alone to be an effective access control mechanism. Consequently, X-Force recommends that organizations securing privileged accounts using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Privileged Access Management (PAM).
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an authentication mechanism that grants access to a security principal only after providing two or more verification factors to confirm their identity and allow authentication to a computer system. MFA will enable organizations to enhance protection against credential theft. Implementing an MFA solution to enhance security in scenarios where the risk of compromised credential use is the greatest, such as:
- Users accessing systems via the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
- Privileged users who are an appealing target for credential harvesting attacks necessary to escalate privileges
- VPN users that internal network from the Internet or other untrusted networks
- Users accessing corporate resources exposed to the internet, such as O365 webmail
PAM is a security technology allowing organizations to manage and secure the credentials for privileged accounts, including users with elevated privileges, local and Active Directory (AD) accounts, system administrators and super users, service accounts, and application accounts, among others. PAM reduces the risk of credential harvesting by malicious threat actors by providing temporary, session-specific credentials to perform a specific task.
At a minimum, X-Force recommends organizations enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for privileged accounts. This would include domain, enterprise, and local administrators.
Prohibit Workstation Logon with Domain Admin Credentials
X-Force recommends organizations implement a Group Policy to prevent workstation login by Domain Admin credentials. The following high-level steps are recommended by Microsoft to complete this recommendation.
In GPOs linked to OUs containing member servers and workstations in each domain, the DA group should be added to the following user rights in Computer ConfigurationPoliciesWindows SettingsSecurity SettingsLocal PoliciesUser Rights Assignments:
- Deny access to this computer from the network
- Deny log on as a batch job
- Deny log on as a service
- Deny log on locally
- Deny log on through Remote Desktop Services user rights
Detailed information on prohibiting Domain Administrator Login to workstations is available on the following webpage:
Restrict SMB/RDP/RPC for Internal Communication
Review the need for and restrict where possible SMB, RDP, and RPC connections between internal VLANS, subnets, or class of system such as:
- Review the need for these protocols between workstations and block/deny these connections if possible.
- SMB and RPC are often required for client/server services and applications however, X-Force recommends organizations determine which services/applications require these protocols and scope firewall rules to accommodate and block/deny all unmercenary connections.
- Deploy dedicated administrative systems (i.e. “jump systems”) to facilitate necessary administrative uses for RDP, SMB, and RPC connections to workstations and servers. At a minimum, X-Force recommends Domain Controllers only be accessible via RDP from specific administrative systems.
Implement Managed Service Accounts
A service account, which can be either a local or domain account, often refers to a user account that provides a security context for services running on a Windows system. Windows offers the following built-in accounts to run services:
- Local system
- Local service
- Network service
System administrators often create service accounts to define specific security privileges for an application instead of using the build-in accounts. Another use case for service accounts is where a single identity is required by multiple systems.
Service accounts often have inherent risks associated with them, such as non-expiring passwords and interactive logons enabled. To address password management issues and prevent interactive logons with service accounts, a solution is to create and use a group Managed Service Account (gMSA). The primary advantage of this approach is that Windows handles password management and rotates the password periodically. Furthermore, a gMSA provides a single identity solution for services running on a server farm, or on systems behind Network Load Balancer. System administrators can configure services to use the new gMSA principal.
In cases where gMSAs cannot be implemented, X-Force recommends configuring security restrictions for regular accounts used as service accounts, including:
- Enforcing the principle of least privilege by assigning the minimum privileges required by the service.
- Denying interactive logons.
- Enforcing a minimum password length of 64 characters.
- Restricting the use of those accounts to the systems and tasks that require those accounts.
The above recommendations can be implemented via the built in Group Policy Object (GPO) functionality within Active Directory.
Restrict Software Execution on Domain Controllers and Secure Administrative Systems
X-Force recommends organizations to design application control policies for Domain Controllers, and secure administrative hosts and enforces those policies through an application whitelisting solution.
Microsoft AppLocker is a built-in application allow list technology that allows organizations to control what software can execute on Windows systems based on attributes, such as executable file path, hash, and publisher. The files that AppLocker can restrict includes executable files, dynamic-link library (DLL) files, Windows installer files, packaged apps, and scripts.
X-Force recommends organizations to design application control policies for Domain Controllers and secure administrative hosts and enforces those policies through AppLocker and Group Policy Objects (GPO) to protect those hosts against unwanted software or unauthorized execution, including malware and attacker utilities.
System administrators must configure an explicit rule and enforce it through a Group Policy for specific software to execute on systems. Any software that is not explicitly allowed will be denied by default. Consider the following approach to minimize the risk of operational impact:
- Configure AppLocker in an audit mode, review logs, and gradually tune application control policies before switching to an enforcement mode.
- Understand the enforcement mode’s impact by configuring audit mode and regularly reviewing event logs to understand what software AppLocker would block in the enforcement mode.
- Consider sending AppLocker audit logs to SIEM and creating rules to alert on unauthorized software, such as PsExec or other known legitimate tools commonly leveraged by threat actors.
https://securityintelligence.com/posts/analysis-of-ransomware/
State of API Security Activity
A recap of API threat statistics and unique threat patterns observed by the Cequence CQ Prime Threat Research Team.

Summary of Key Findings
- Unusual uptick in traffic from China spiking at a 200% increase
- User-experience business logic was abused to commit fraudulent purchases on stolen cards
- Pop in traffic from a holding company for scraping and hosting services
API Security Trends Observed
Between late February and early April 2022, the Cequence #API Security Platform mitigated 108 million ATO attempts, using behavioral fingerprints and blocking millions of malicious IP addresses and organizations. During that same timeframe, the Cequence CQ Prime Threat Research Team observed an unusual uptick in traffic from China across the board, bucking the common bot tactic of blending in with normal traffic. In early March, the team tracked a sophisticated recon effort as a threat actor abused e-commerce user-experience business logic to attempt to commit fraudulent purchases on stolen credit cards through automated account creation. Finally, the team observed a notable pop in traffic from an organization Emeigh Investments LLC which appears to be the holding company for a set of scraping & hosting services.
Uptick in Traffic from China
To ensure their bot achieves its end goal, threat actors will typically make every effort to hide their bot traffic within legitimate end user requests. This means following the same buying process a user follows, funneling traffic through local, residential proxies, and so on. The Cequence CQ Prime Threat Research Team observed a steady uptick in traffic from China beginning in February and spiking at a 200% increase in early March. This pattern deviates from the hide in plain sight approach that bots typically follow, given the target customers were in the US and EMEA and did not transact much business with customers in China.
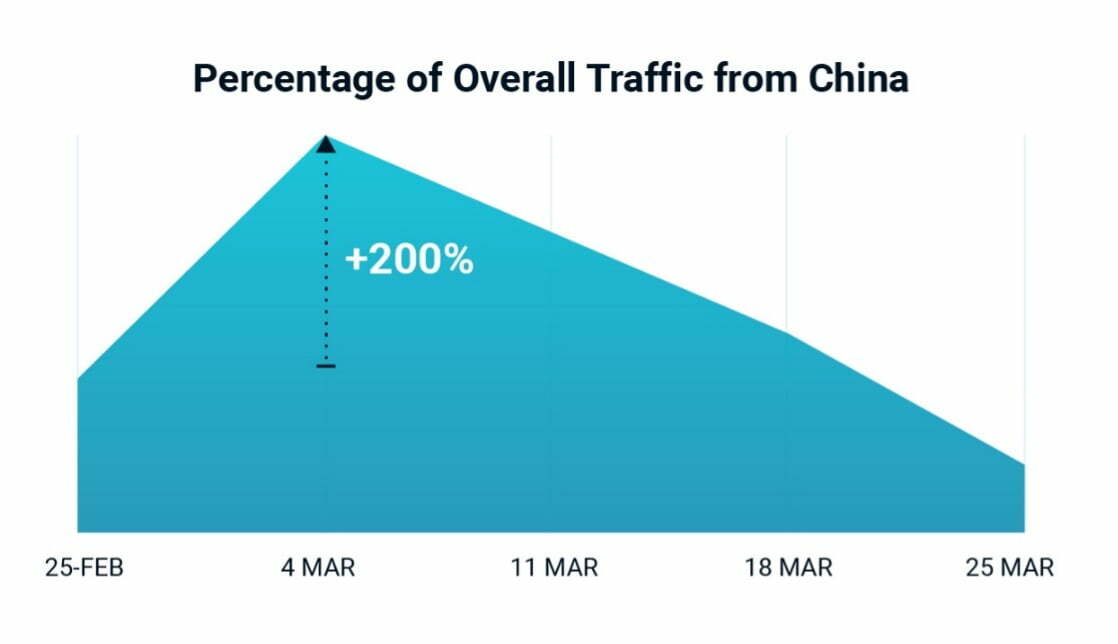 Image 1: Uptick in malicious traffic from China as a percentage of overall.
Image 1: Uptick in malicious traffic from China as a percentage of overall.
While the overall volume of traffic from China is small, the uptick shown in image 1 is worth noting as it was observed across multiple customers in the US and EMEA.
- Account takeover was the most common attack type observed within the traffic from China with roughly 600K ATO attempts emanating from China detected and blocked while protecting 265K unique user accounts, resulting in a customer savings of $1.46M, based on the Juniper Research report that states ATOs cost an average of $290 per account.
- One of the patterns observed saw the threat actor rotate across multiple login API endpoints on 15 minute intervals with traffic bursts of up to 80% of the normal traffic volume of a given API. At least 10 different Behavioral Fingerprints were triggered, representing signs of automation such as the same userID on many different IP addresses, further confirming that this was an automated.
- Attack traffic was distributed across 400K IPs from 168 organizations with most common being China Telecom, 189.cn, China Telecom Jiangx, CHINATELECOM Xinjiang Wulumuqi MAN network and Chunghwa Telecom.
Sophisticated Reconnaissance
In an example of how dedicated threat actors are, the Cequence CQ Prime Threat Research team observed an attacker methodically map a customer’s entire site to learn the precise workflow and uncover any potential weaknesses. The threat actor created an account then tested how it could be abused with an end goal of gift card fraud or fradulent purchases using stolen credit cards. The weaknesses the attacker exploited are common in online retail environments where important decisions regarding the tradeoff between shopper experience and security must be made. In this case, the attacker found that the account creation workflow would immediately authenticate, and authorize a user to do subsequent privileged actions like edit/change payment details. From an end-user perspective, this flow makes sense to reduce user friction for recently created accounts. However attackers realized they could use bots to abuse this business logic, and create accounts en masse. The attacker was committed to remaining undetected as they distributed more than 1.5M requests across 132,660 IPs from 20+ organizations. Ultimately, the attack triggered hundreds of Behavioral Fingerprints representing actions including use of outdated browsers, malicious traffic source, and rapid user-agent rotation.
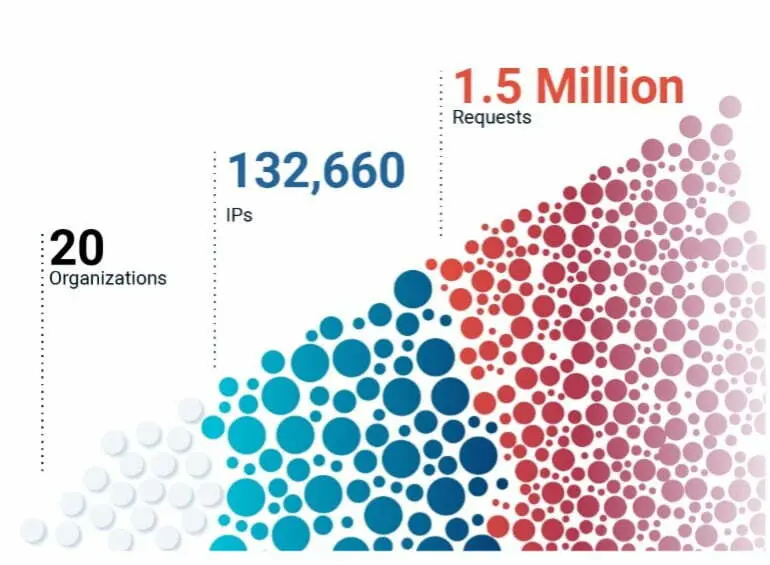
Image 2: Malicious traffic observed during a sophisticated reconnaissance effort.
New Bulletproof Proxy Provider?
The threat team observed an ATO attack that encompassed 8.7M requests distributed across 1.1M residential proxies from 20 or so organizations. The threat actor rapidly retooled, triggering hundreds of Behavioral Fingerprints with actions that include many user names logging in from same IP, too many account verification attempts from same IP and same userid accessed over multiple IP addresses. One of the interesting characteristics of this attack is the emergence of a new organization as the source for malicious traffic. While only a small percentage of the traffic, the threat team observed a spike in use from Emeigh Investments LLC, a holding company for Sprious (https://sprious.com/), which names Blazing SEO (https://blazingseollc.com/), Scraping Robot, (https://scrapingrobot.com/) and WP Super Host (https://wpsuperhost.com/) as partner companies. The likely source of the IP addresses is Blazing SEO, given that their product line includes both data center and residential proxy offerings. The spike is of interest because of the somewhat sudden appearance as a top source of malicious traffic. As noted in the chart, they were more heavily used then Cogent and ServerMania – two sources that are constantly at the top of the list of organizations whose infrastructure is used in automated attacks against our customers.
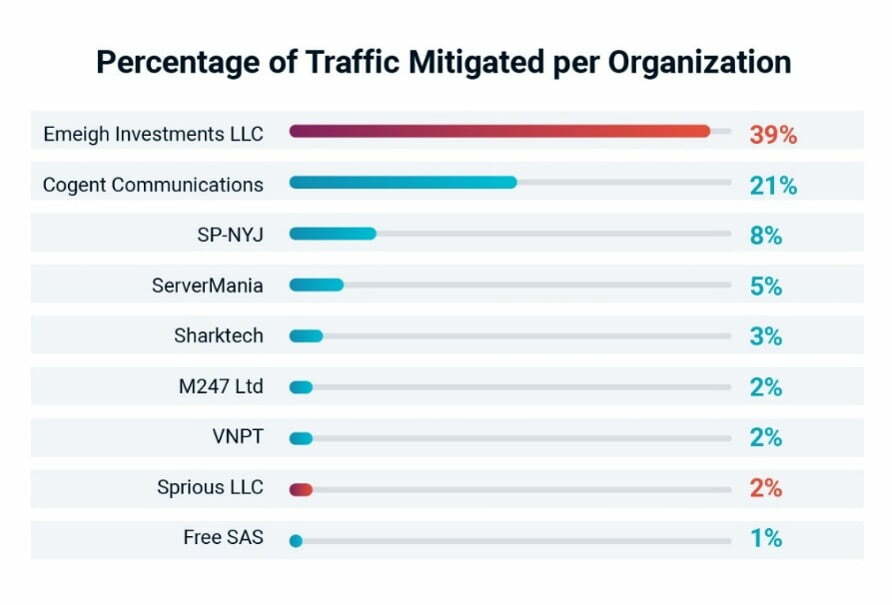
Image 3: A potentially new Bulletproof Proxy vendor appeared in Q1 2022.
As documented in our ongoing research on Bulletproof Proxies, these vendors walk a thin line between legitimate and malicious use. Their services can certainly be of benefit to web masters and marketing teams who wish to test the performance of their web site. However, their tools are commonly used as integral elements of an automated attack. For a very low cost, a bot manager can subscribe to their services and easily distribute their attack across many, many IP addresses from a range of cities, states and countries. All with the end goal of masking identity and location while achieving scale.
https://www.cequence.ai/blog/state-of-api-security-activity/
Voice Biometrics Market Size Worth $4.82Bn, Globally, by 2028 at 20.6% CAGR – Exclusive Report by The Insight Partners
NEW YORK , May 23, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — The Insight Partners published latest research study on “Voice Biometrics Market Forecast to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis – by Component (Solution and Services), Type (Active #Voice Biometrics and Passive Voice #Biometrics), Authentication Process (Automated IVR, Agent-assisted, Mobile Application, and Employee Authentication), Deployment (Cloud and On-premise), Vertical (BFSI, Retail & Commerce, Government & Defense, IT & Telecom, Healthcare & Life Sciences, Transportation & Logistics, Travel & Hospitality, Energy & Utilities, and Others), and Application (Authentication & Customer Verification, Forensic Voice Analysis & Criminal Investigation, Fraud Detection & Prevention, Risk & Emergency Management, Transaction Processing, Access Control, Workforce Management, and Others)”, the global voice biometrics market share is expected to grow from $1.31 Billion in 2021 to $4.82 Billion by 2028; it is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 20.6% from 2022 to 2028.
The Sample Pages Showcases Content Structure and Nature of Information Included in This Research Study Which Presents A Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis: https://www.theinsightpartners.com/sample/TIPRE00004086/
|
Report Coverage |
Details |
|
#Market Size Value in |
US$ 1.31 Billion in 2021 |
|
Market Size Value by |
US$ 4.82 Billion by 2028 |
|
Growth rate |
CAGR of 20.6% from 2022 to 2028. |
|
Forecast Period |
2022-2028 |
|
Base Year |
2022 |
|
No. of Pages |
238 |
|
No. Tables |
165 |
|
No. of Charts & Figures |
120 |
|
Historical data available |
Yes |
|
Segments covered |
Component, Type, Authentication Process, Deployment, Vertical, and Application |
|
Regional scope |
North America; Europe; Asia Pacific; Latin America; MEA |
|
Country scope |
US, UK, Canada, Germany, France, Italy, Australia, Russia, China, Japan, South Korea, Saudi Arabia, Brazil, Argentina |
|
Report coverage |
Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
Voice Biometrics Market: Competitive Landscape and Key Developments
Aculab; Auraya, Inc; Aware Inc; Nuance Communications, Inc; Nice; Pindrop; Phonexia; SESTEK; Whispeak; and VERINT SYSTEMS INC are among the key players in the global Voice Biometrics market. The leading companies are focusing on expanding and diversifying their market presence and acquiring a new customer base, thereby tapping prevailing business opportunities.
Schedule A Pre-Sale Discussion with The Author Team in A Slot That You Prefer to Address Queries on Scope of The Study, Customization, Introduction to Research Methodology, Assistance on Technologies and Market Definitions: https://www.theinsightpartners.com/inquiry/TIPRE00004086/
In January 2022, Aware, Inc. entered into a strategic partnership with MIRACL, cybersecurity company specialized in single step, secure multi factor authentication.
The rise of modern technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), cloud computing, and data analytics and the strong demand for preserving healthcare and financial data is propelling the growth of the voice biometrics market. End-use industries such as banking, financial services and insurance (BFSI), government and public sectors, and IT & telecom are experiencing growth due to increasing urbanization and digitalization worldwide. As a result, hackers are targeting the important information and resources used in these areas. Further, biometrics used as credentials require the usage of unalterable, robust, and extensive algorithms to validate individuals. The advantages of biometric authentication over speech recognition and the promising development of AI-based voice recognition technology that reduces the risk of replication or hacking provide top-notch biometric security
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Global Voice Biometrics Market:
In 2020, the impact of the COVID-19 outbreak differed in every country across the European region, as few countries witnessed an increased number of recorded cases and subsequently faced strict and longer lockdown periods or social isolation. However, COVID-19 impact on Western European countries such as Germany, France, and the UK was comparatively moderate due to their robust healthcare systems. To protect citizens from the virus, the European governments made tremendous investments in incorporating technologies in healthcare systems to help identify signs of the COVID-19 virus. In 2021, the offices resumed operations due to a reduction in lockdown measures and an increased vaccination process.
However, manufacturers were obliged to focus more on contactless biometrics technology over the last two years due to escalating hygiene concerns and the increased danger of the COVID-19 pandemic. Further, industry players are currently concentrating more on developing biometric systems based on touchless technologies such as the face, iris, vein, and voice recognition to maintain their position in the voice biometrics market.
Growing Demand for Fraud Detection and Prevention System to Propel Voice Biometrics Market Growth in Coming Years:
Banks constantly remain on top of the best authentication methods to combat online fraud. Authentication mechanisms based on knowledge, such as PINs, passwords, and one-time passwords, have been employed by banks in the past. Further, banking security was affected by the demand for contactless and seamless technologies due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
With the advent of digitization in the financial business, fraudulent activities are expanding alarmingly. Fraudsters with access to banking credentials get access to clients’ bank accounts due to high-profile data thefts, necessitating a second or third degree of protection in the entire financial authentication system. Banks and financial institutions benefit from speech biometrics technologies that intelligently identify users based on their voiceprints.
Have A 15-Minute-Long Discussion with The Lead Research Analyst and Author of The Report in A Time Slot Decided by You. You Will Be Briefed About the Contents of The Report and Queries Regarding the Scope of The Document Will Be Addressed as Well: https://www.theinsightpartners.com/speak-to-analyst/TIPRE00004086
The voice biometrics market simplifies market user identification and authentication while improving Know Your Customer (KYC) management due to automatic calibration, active and passive authentication, liveliness detection, and panic detection. For example, Barclays uses the phrase “My voice is my password” to verify the caller’s identification, which resulted in a 20-second reduction in user verification time. Similarly, prominent banks such as HSBC, Wells Fargo, Santander Bank, N. A., and Tangerine Bank are implementing speech recognition in their call centers to speed up the identification and verification process. Further, the voice biometrics market potentially helps to improve KYC procedures. People in multilingual countries such as South Asia, for instance, have diverse degrees of schooling in different parts of the country. Moreover, voice biometrics help includes such persons in a financial safety net because the solutions are language-independent. Thus, the growing demand for fraud detection and prevention system in the BFSI industry is driving the growth of the voice biometrics market.
Voice Biometrics Market: Authentication Process Overview
Based on authentication process, the voice biometrics market is segmented into automated IVR agent-assisted, mobile applications, and employee authentication. In 2021, the agent-assisted segment held the largest voice biometrics market share.
Immediate Delivery of Our Off-The-Shelf Reports and Latest Research Studies, Through Flexible and Convenient Payment Methods: https://www.theinsightpartners.com/buy/TIPRE00004086/
Browse Adjoining Reports:
Biometrics Technologies Market to 2027 – Global Analysis and Forecasts by Retail Type (Pre-Boarding and Post-Boarding); Shopping Type (Accessories, Alcohol, Beauty Products, Merchandise, and Others); Carrier Type (Full Service Carrier and Low Cost Carrier)
Biometrics Market Forecast to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis By Component (Hardware, Software); Application (Authentication, Access Control); End-User Industry (Government, Military and Defense, Healthcare, BFSI, Consumer Electronics, Travel and Immigration, Others) and Geography
Fraud Detection and Prevention Market Forecast to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis By Component (Solution and Services), Deployment (On-premises and Cloud), and End-user (BFSI, Healthcare, Manufacturing, Retail, Telecommunication, and Others)
Voice Analytics Market Forecast to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis By Component (Solution, Service); Deployment Mode (On-Premise, Cloud); Application (Call Monitoring, Sentiment Analysis, Risk and Fraud Detection, Others); End User Industry (Retail and Ecommerce, BFSI, Government, IT and Telecom, Others) and Geography
Treasury and Risk Management Market Forecast to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis – by Component (Solution and Services), Deployment (Cloud-based and On-premises), Enterprise Size (Small & Medium-Size Enterprises and Large Enterprises), Application (Account Management, Cash & Liquidity Management, Compliance & Risk Management, and Financial Resource Management), and End User (BFSI, IT & Telecom, Retail & E-commerce, Healthcare, Manufacturing & Automotive, and Others)
Advanced Authentication Market Forecast to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis By Authentication Methods (Smart Cards, Biometrics, Mobile Smart Credentials, Tokens, User-based Public Key Infrastructure, Other); End User (BFSI, Healthcare, Government, Defense, IT and Telecom, Other) and Geography
Incident and Emergency Management Market Forecast to 2028 – COVID-19 Impact and Global Analysis by Component (Solution, Service, Communication System); Vertical (Commercial and Industrial, Energy and Utilities, Healthcare and Life Sciences, Defense and Military, Transportation and Logistics, Government, Others) and Geography
Access Control Market to 2025 – Global Analysis and Forecasts by Type (Hardware, Software, and Services) and Application (BFSI, Residential, Commercial, Healthcare, Government & Transport, and Others)
Audio Communication Monitoring Market Forecast to 2028 – Covid-19 Impact and Global Analysis – by Solution & Service (Quality Analysis, Voice Biometric System, Loudness Metering & Monitoring, and Support and Maintenance Services); Enterprise (Small & Medium Enterprise and Large Enterprise); and Application (Transportation & Logistics, Government, Telecommunication & IT, Healthcare, Media & Entertainment, BFSI and Others)
About Us:
The Insight Partners is a one stop industry research provider of actionable intelligence. We help our clients in getting solutions to their research requirements through our syndicated and consulting research services. We specialize in industries such as Semiconductor and Electronics, Aerospace and Defense, Automotive and Transportation, Biotechnology, Healthcare IT, Manufacturing and Construction, Medical Device, Technology, Media and Telecommunications, Chemicals and Materials.
Contact Us:
If you have any queries about this report or if you would like further information, please contact us:
Contact Person: Sameer Joshi
E-mail: sales@theinsightpartners.com
Phone: +1-646-491-9876
Press Release: https://www.theinsightpartners.com/pr/voice-biometrics-market
SOURCE The Insight Partners